

In the wonderful world of chemistry, every single compound is identified in its own special way. This is done using a system called the Chemical Abstracts Service (CAS) number. This system provides a unique identifier for each and every chemical substance.
Among these, CAS number 25340-17-4 is a really important compound with lots of different uses across lots of different industries. Understanding this compound is a real eye-opener! It not only reveals its chemical identity, but also shows us just how important it is in fields as diverse as manufacturing and pharmaceuticals. If your business has a need for this compound, we have also recommended a manufacturer that can meet your requirements.
In this blog, we'll be taking a closer look at what CAS 25340-17-4 is, its many uses, safety considerations and the rules that govern its use. Join us as we explore the fascinating details of this chemical and discover its vital role in modern science and industry!
The Chemical Abstracts Service (CAS) number is a unique identifier assigned to every chemical substance described in the CAS database, which is maintained by the American Chemical Society. This numerical identifier, typically consisting of up to ten digits grouped in three sections separated by hyphens, facilitates the precise identification of chemical compounds across various industries, including pharmaceuticals, chemistry, and regulatory affairs.
CAS numbers serve as a standardized means of reference, allowing for the unambiguous communication of chemical information regardless of the substance's name, synonym, or structural representation. Each CAS number corresponds to a single chemical entity, which can include organic and inorganic compounds, polymers, biological sequences, and other substances. The use of CAS numbers is crucial for ensuring accuracy in safety data sheets, regulatory documentation, and research literature, enabling stakeholders to efficiently locate and reference specific chemical substances in a global context. This systematic approach is vital for compliance with regulatory frameworks, facilitating research and development, and promoting safety in handling and usage of chemicals.
CAS Number 25340-17-4 refers to the chemical substance Diethylbenzene, a group of organic compounds primarily used as solvents and intermediates in the production of various chemical products. It is a colorless liquid that is insoluble in water but miscible with most organic solvents.
The chemical formula of diethylbenzene is C10H14 and it belongs to the family of aromatic hydrocarbons known for their stability and resonance structure. This compound exists in several isomeric forms, with the most common being ortho-, meta-, and para-diethylbenzene.
Each isomer has distinct properties and applications.
Chemical products, such as diethylbenzenes, are substances produced through chemical processes. They play a crucial role in the chemical industry, acting as raw materials, intermediates, and finished goods. In the chemical industry, diethylbenzenes serve as important raw materials in the synthesis of polymers, resins, and other materials. They are commonly utilized in the production of plastics, adhesives, and coatings, contributing significantly to the manufacturing processes across various sectors. Furthermore, due to its role as a solvent and reaction medium, diethylbenzene contributes to the manufacturing of a wide range of industrial and consumer products.
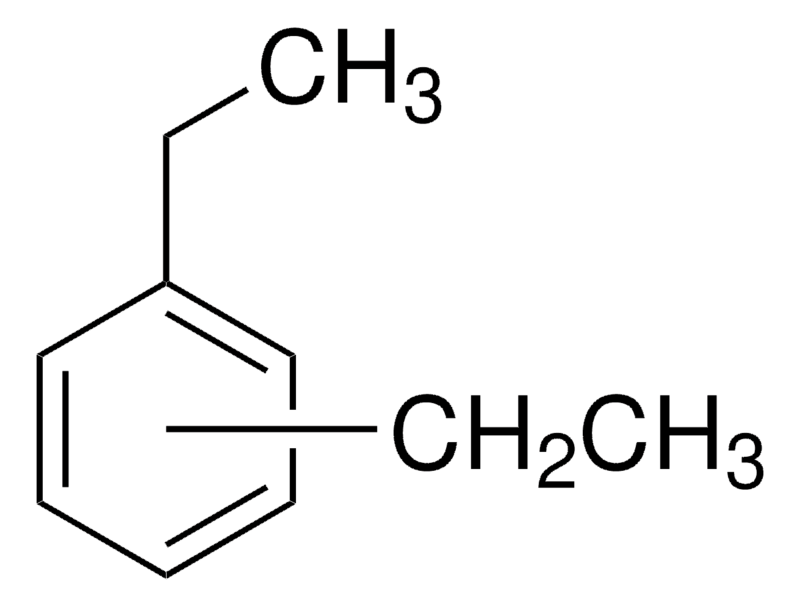
Diethylbenzene is an organic compound with the chemical formula C10H14.
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Chemical Formula | C10H14 |
| Molecular Weight | 130.23 g/mol |
| Appearance | Colorless liquid |
| Odor | Pungent, similar to garlic |
| Boiling Point | 183 - 184 °C |
| Melting Point | -95.5 °C |
| Density | 0.860 g/cm³ |
| Solubility in Water | Slightly soluble |
| Flash Point | 33 °C (91 °F) |
| Viscosity | 1.05 mPa·s at 25 °C |
| Refractive Index | 1.484 - 1.488 |
| Partition Coefficient (Log P) | 3.73 |
Diethylbenzene is typically produced through the alkylation reaction of benzene with ethylene in the presence of a suitable catalyst, such as aluminum chloride or hydrofluoric acid. This process involves the introduction of ethyl groups onto the benzene ring, resulting in the formation of diethylbenzene as the primary product. The production scale and efficiency of this process are key factors influencing the availability and cost of diethylbenzene in the market.
Always wear appropriate PPE, including gloves, goggles, and chemical-resistant clothing, to prevent skin and eye contact.
Ensure adequate ventilation in the work area to minimize inhalation of vapors. Use fume hoods or local exhaust systems when handling diethylbenzene.
Keep diethylbenzene away from open flames, sparks, and other ignition sources, as it is flammable.
Store diethylbenzene in tightly sealed containers made of compatible materials, such as glass or specific plastics, to prevent leakage and contamination.
Clearly label all containers with the chemical name, CAS number (25340-17-4), and hazard warnings to ensure proper identification.
Store in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight and heat sources. The recommended storage temperature is typically below 25°C (77°F).
Keep diethylbenzene separate from incompatible materials, such as strong oxidizers, acids, and bases, to prevent dangerous reactions.
Store in a designated flammable liquids storage area, equipped with fire extinguishers and emergency response equipment.
Conduct routine inspections of storage areas and containers to check for leaks, damage, or signs of deterioration.
Diethylbenzene (CAS Number 25340-17-4) is an aromatic hydrocarbon that, like other industrial chemicals, poses potential environmental risks. Understanding its environmental impact is crucial for responsible handling and regulation.
When released into the environment, whether through air emissions, water discharge, or soil contamination, Diethylbenzene poses risks to both the ecosystem and human health.
While diethylbenzene is a valuable industrial chemical, its environmental impact cannot be overlooked. Responsible handling, storage, and disposal are essential to mitigate its potential risks to air, water, and soil quality.
When choosing a diethylbenzene manufacturer, it's important to consider several factors to ensure you're working with a reliable and efficient supplier. One outstanding option is High Mountain Chem, a professional industrial company specializing in the production of speciality chemicals, including diethylbenzene. Here's why High Mountain Chem could be the ideal choice for your needs:
For further inquiries or to discuss your specific needs, feel free to contact their team.
In conclusion, CAS Number 25340-17-4, or diethylbenzene, is essential in the chemical industry due to its unique properties and wide-ranging applications. It serves as a key precursor for producing styrene and other specialty chemicals, significantly contributing to the efficiency of various industrial processes.
Diethylbenzene's role in formulating resins and plastics supports innovation across multiple sectors, including automotive and construction. However, it’s important to address its potential environmental impact through responsible handling and adherence to safety regulations.
Click here to get a free consultation for diethybenzenes.









