
_1730361664_WNo_1600d900.jpg)
Diving into the world of chemical compounds, we often encounter substances that play pivotal roles in various industries. One such compound is Methyl Chloroacetate, identified by the CAS Number 96-34-4.
This versatile chemical intermediate is not just a number on a label but a key component in a myriad of applications, from pharmaceuticals to agrochemicals.
If your enterprise has a demand for this chemical workhorse, we've also identified a reputable manufacturer who can meet your needs with quality and reliability.
A CAS Number, or Chemical Abstracts Service Number, is a unique numerical identifier assigned to chemical substances, allowing precise identification among millions of compounds. Typically formatted with up to 10 digits in three parts (e.g., 123-45-6), CAS Numbers facilitate standardized communication in fields such as chemistry, pharmaceuticals, and manufacturing. They are recognized globally, helping to avoid confusion from common names and synonyms. Many regulatory agencies, like the EPA and OSHA, require CAS Numbers for compliance documentation, aiding in the classification and monitoring of substances for safety and environmental impact. Researchers use CAS Numbers for literature searches, enabling quick access to information about specific compounds, including their properties and applications.
Overall, CAS Numbers play a crucial role in ensuring reliable identification and communication within the chemical industry.
CAS Numbers provide a clear and unambiguous way to identify chemical substances. This is particularly important in industries where multiple compounds may share similar names or chemical formulas. By using CAS Numbers, researchers and professionals can avoid confusion and ensure they are referring to the correct substance.
CAS Numbers are used internationally across various industries, including pharmaceuticals, agriculture, and manufacturing. This standardization facilitates communication between different stakeholders, such as manufacturers, suppliers, and regulatory agencies.
Many regulatory frameworks require the use of CAS Numbers for reporting and compliance purposes. For example, in the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) and the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) often use CAS Numbers in their regulations. This helps ensure that substances are correctly categorized and monitored for safety and environmental impact.
In research and development, CAS Numbers play a critical role in literature searches, patent applications, and product formulations. Scientists and researchers can quickly locate information about a specific compound, including its properties, safety data, and potential applications.
Companies use CAS Numbers to manage chemical inventories and streamline supply chain processes. By organizing substances by their CAS Numbers, businesses can efficiently track usage, reorder materials, and maintain compliance with safety regulations.
CAS Numbers are essential in safety data sheets (SDS) and material safety data sheets (MSDS). These documents provide critical information about the hazards and safe handling procedures for specific substances, ensuring that workers are informed and protected.
CAS Numbers are used in the chemical industry to identify and communicate about chemical substances. They are important for following the rules, doing research and keeping people safe. This makes them useful for professionals in different areas.
CAS Number 96-34-4 refers to the chemical substance Methyl Chloroacetate, an organic compound primarily utilized as an intermediate in organic synthesis. It appears as a colorless to yellowish liquid with a sweet, fruity odor, and is soluble in organic solvents like ether and alcohol.
The chemical formula of Methyl Chloroacetate is C3H5ClO2. This compound features a chloroacetate group, which contributes to its reactivity and makes it a valuable building block in the synthesis of various chemicals.
Methyl Chloroacetate is significant in the chemical industry, serving as a precursor in the production of pharmaceuticals and agrochemicals. It is commonly used to synthesize bioactive compounds, including anti-inflammatory and analgesic agents. Additionally, it finds applications in the manufacture of esters utilized in fragrances and flavors.
Due to its reactivity, Methyl Chloroacetate plays an essential role in organic synthesis, facilitating the formation of various chemical structures. Its importance in multiple sectors, including pharmaceuticals and specialty chemicals, underscores its versatility and utility in manufacturing processes. However, safety precautions are necessary when handling this compound due to its potential hazards.
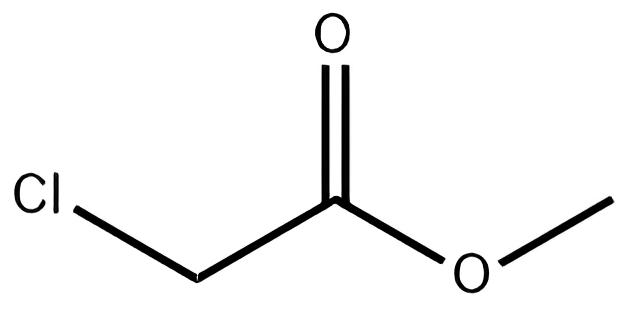
Methyl Chloroacetate's physical and chemical properties, including its melting and boiling points, density, and solubility, make it a valuable compound in organic synthesis and industrial applications.
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Chemical Formula | C3H5ClO2 |
| Molecular Weight | 110.53 g/mol |
| Appearance | Colorless, transparent liquid |
| Odor | Sweet, fruity |
| Boiling Point | 130 °C (740 mmHg) |
| Melting Point | -33 °C |
| Density | 1.238 g/cm³ at 25 °C |
| Solubility in Water | 28 g/L at 20 °C; 51 g/L (slow decomposition) |
| Flash Point | 125 °F (approximately 52 °C) |
| Refractive Index | 1.422 at 20 °C |
| pH | 4.6 (28 g/L in H₂O at 20 °C) |
| Partition Coefficient (Log P) | 0.63 at 20 °C |
Methanol and chloroacetic acid are mixed uniformly in a weight ratio of 0.366:1 and stirred while being heated. The esterification reaction is carried out at a temperature of 105-110 °C. During the reaction, a ternary azeotrope of methyl chloroacetate, water, and methanol is continuously distilled off. The resulting layers are separated in an ester separator, with the separated methanol and water being refluxed back into the reaction vessel. The crude ester obtained is neutralized with sodium carbonate.
After neutralization, the crude ester is first distilled at atmospheric pressure to collect the fraction at 130 °C, followed by a reduced-pressure distillation to collect the fraction at 65 °C (8 kPa), which constitutes the finished Methyl Chloroacetate product. The yield is approximately 96%. When used as a pesticide intermediate, the crude ester can be washed with water and neutralized to obtain a product with over 95% purity, which can be used directly.
To produce 1 ton of Methyl Chloroacetate of this specification, approximately 800 kg of chloroacetic acid and 330 kg of methanol are consumed. In laboratory preparations, concentrated sulfuric acid is often added dropwise to the chloroacetic acid and methanol mixture, followed by heating and refluxing for 5 hours, and then neutralization, water washing, drying, and reduced-pressure distillation to obtain the final product.
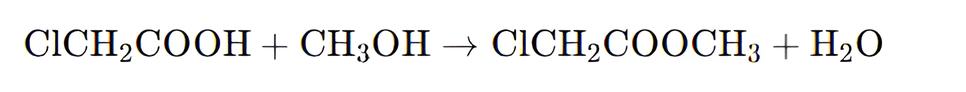
Methyl chloroacetate (CAS Number 96-34-4) is an organic compound that finds application across several industrial sectors due to its versatile chemical properties. Here are some of its key industrial applications:
These applications underscore the importance of methyl chloroacetate in a range of industries, from pharmaceuticals to agriculture, where its unique chemical properties enable the production of a variety of essential goods and intermediates.

This picture is provided solely for illustration purposes. Optical properties of the actual product may deviate. Relevant product information is printed on labeled products and other accompanying or available information material.
This image depicts SKU: 108413-1KG.
Safe handling and storage of Methyl chloroacetate (CAS Number 96-34-4) is crucial due to its hazardous properties. Here are the key guidelines based on the safety data sheets and expert advice:
- Wear protective gloves, eye protection, and face protection to prevent contact with skin and eyes .
- Respiratory protection is necessary when vapors or aerosols are generated .
- Ensure adequate ventilation, especially in confined areas, to prevent the buildup of vapors .
- Work under a hood to avoid inhalation of the substance or mixture .
- Avoid rough handling of containers to prevent leakage, overflow, or scattering .
- Take necessary actions to avoid static electricity discharge, which might cause ignition of organic vapors .
- Do not eat, drink, or smoke when using this product .

- Store in a well-ventilated place, away from heat, hot surfaces, sparks, open flames, and other ignition sources .
- Keep container tightly closed in a dry place, protected from light, and away from sources of ignition .
- Store below +15°C (+59°F) .
- Methyl chloroacetate should not come into contact with reducing agents, strong acids, strong bases, aluminum, copper, or oxidizing agents, as these can cause hazardous reactions .
- Recycle any unused portion of the material for its approved use or return it to the manufacturer or supplier .
- Ultimate disposal must consider the material's impact on air quality, potential migration in air, soil, or water, and effects on animal, aquatic, and plant life, as well as conformance with environmental and public health regulations .

- In case of a spill, cover drains, collect, bind, and pump off spills, and observe possible material restrictions .
- Use liquid-absorbent materials like Chemizorb® for cleanup and dispose of properly .
- Suitable extinguishing media include water spray (fog), carbon dioxide (CO2), foam, extinguishing powder, and sand .
- Thermal decomposition can lead to the release of irritating and toxic gases and vapors, so special protective actions for firefighters are necessary, including self-contained breathing apparatus and full firefighting turnout gear .
By adhering to these safety and storage guidelines, the risks associated with handling and storing Methyl chloroacetate can be minimized, ensuring the safety of workers and the environment.
Selecting a reliable supplier for Methyl Chloroacetate is critical for ensuring quality, consistency, and value in your supply chain. Here are key factors to consider when choosing a supplier:
One outstanding option is High Mountain Chem, a professional industrial company specializing in the production of speciality chemicals, including methyl chloroacetate.
For further inquiries or to discuss your specific needs, feel free to contact their team.
Methyl Chloroacetate is primarily used as an intermediate in the pharmaceutical and agrochemical industries. It is essential in synthesizing various active pharmaceutical ingredients and chemicals for herbicides and pesticides. Additionally, it finds application as a solvent in the production of plastics, synthetic fibers, and resins.
Buyers should consider the quality and purity of the product, supplier reliability, compliance with regulatory standards, pricing, and the supplier's commitment to sustainability. Evaluating these factors ensures a high-quality product that meets specific needs and aligns with environmental and safety standards.
Want to get the right methyl chloroacetate for your business? Click here to get a free consultation.









